Manufacturing Technology and Processes
Manufacturing is the backbone of any industrial economy, and the technology and processes used in this sector are continually evolving to meet growing demands. With rapid advancements in automation, digitalisation, and materials science, the way products are designed and produced has transformed significantly.
What is Manufacturing Technology?
Manufacturing technology refers to the tools, machines, processes, and systems used in the production of goods. It includes everything from machinery used in factories to computer-aided design (CAD) software and even advanced robotics. The primary aim of manufacturing technology is to improve the speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of production while maintaining high standards of quality.
Key Manufacturing Processes
There are several core manufacturing processes that industries rely on to create products:
- Casting and Moulding
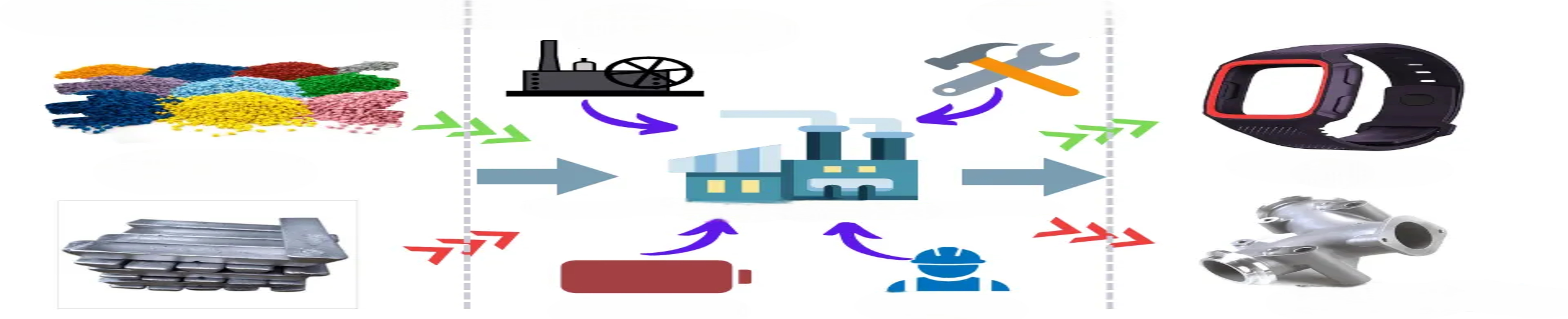
Casting and moulding are traditional methods where materials like metals, plastics, and glass are heated and poured into moulds to form specific shapes. These methods are commonly applied in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and everyday consumer products.
- Machining
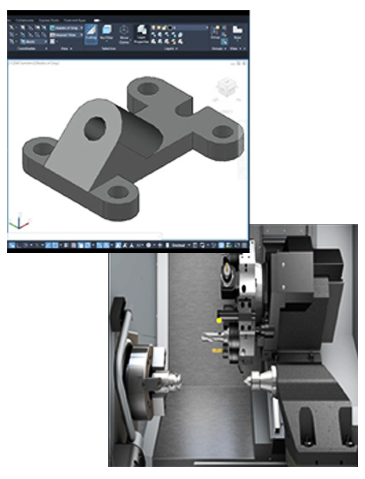
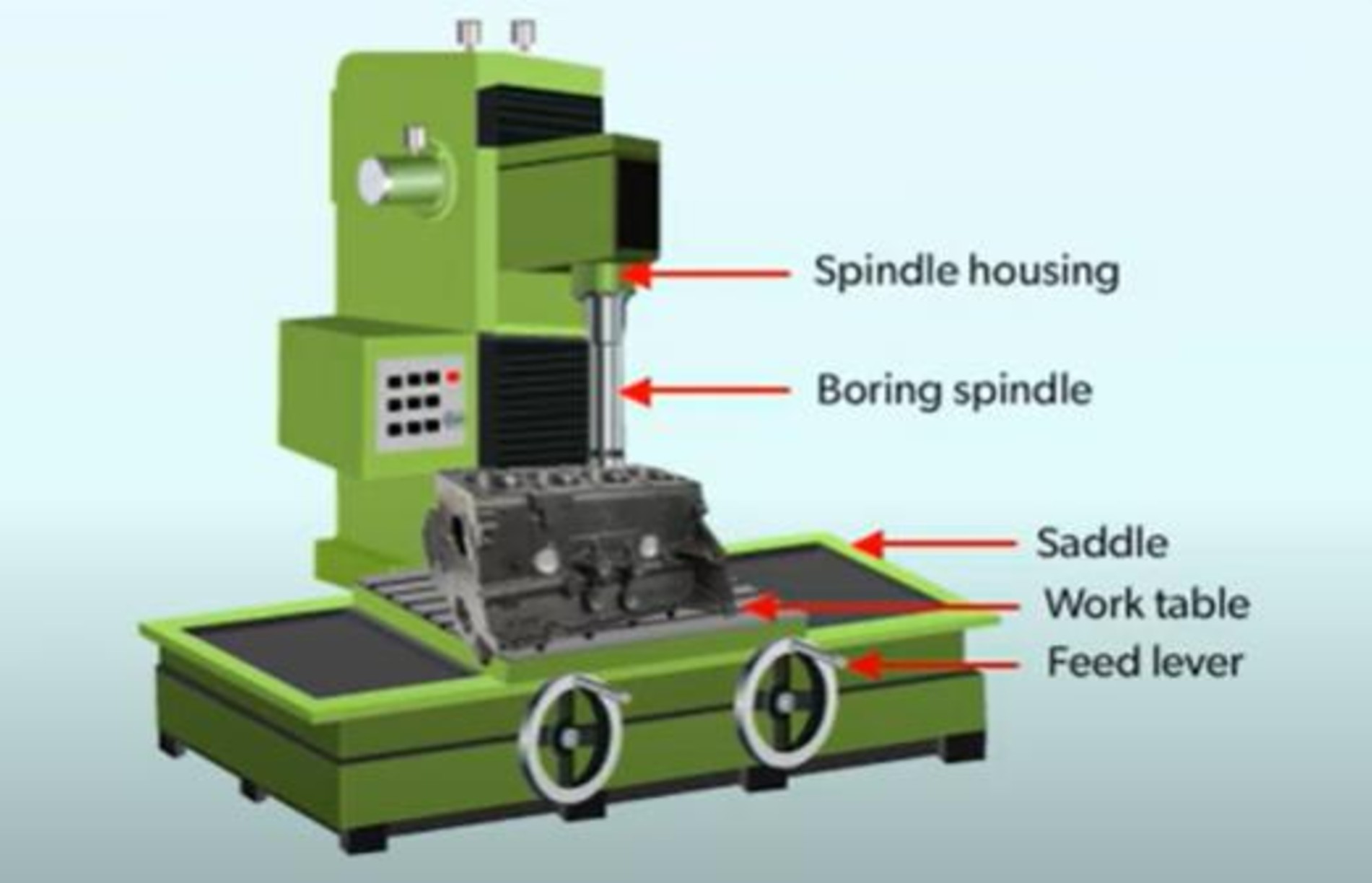
Machining is a precise manufacturing method where specialised cutting tools remove material from a workpiece to create desired shapes. This subtractive process uses equipment like lathes, mills, and CNC machines to transform raw materials into finished components with specific dimensions and surface finishes. It is ideal for producing precise parts like gears, shafts, and housings. Turning, milling, and drilling are among the standard techniques used in machining to create accurate components.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, revolutionises production by building objects layer-by-layer from digital models, enabling complex designs impossible with traditional methods. This process builds up a product layer by layer, offering unprecedented flexibility in design and reducing material waste. It’s ideal for rapid prototyping, customised products, and complex structures.
- Welding and Joining
Welding and joining techniques are used to fuse parts together, whether through traditional methods like arc welding or newer processes like laser welding. These methods are crucial in industries such as construction, automotive, and shipbuilding.
- Forming and Forging
Forming and forging involves shaping materials under high pressure. These processes are commonly used for making strong parts that require structural integrity, such as engine components and frames.
Impact of Modern Manufacturing Technology
- Efficiency and Cost Savings
Modern manufacturing processes make production faster, more precise, and less wasteful. Automation, such as robotics and conveyor systems, allows for continuous production cycles, reducing labour costs and increasing throughput. This efficiency translates to lower costs for manufacturers and consumers alike.
- Customisation and Flexibility
The latest manufacturing technologies, especially 3D printing, have opened up opportunities for mass customisation. Companies can now produce products tailored to specific customer needs without drastically increasing production costs. This flexibility also extends to the design phase, where rapid prototyping allows for quicker testing and iteration of ideas.
- Improved Product Quality
With advanced technologies, manufacturers can maintain tighter tolerances and ensure higher consistency in their products. Automated quality control systems and smart sensors are now widely used to detect defects early in the production process, minimising human error and ensuring that products meet the required standards.
- Sustainability
Sustainability has become a top priority in modern manufacturing. Processes like additive manufacturing reduce material waste, while energy-efficient machinery helps lower carbon footprints. Additionally, the use of renewable materials and recycling technologies in manufacturing is on the rise, contributing to a greener future for industries.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the numerous advantages, there are also challenges in adopting new manufacturing technologies. The initial costs for advanced machinery and training can be significant, and small businesses may struggle to keep up. There’s also a growing demand for trained personnel to handle and maintain modern manufacturing equipment.
Looking ahead, manufacturing will continue to evolve with advancements like AI-driven automation, IOT-enabled factories, and improved materials. Industries will need to adapt to these innovations, balancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality.
Conclusion
Manufacturing technology and processes play a crucial role in shaping modern industries. From increasing efficiency and reducing costs to enabling customisation and improving product quality, these innovations are transforming how products are made. As industries continue to evolve, keeping up with the latest advancements in manufacturing technology will be key to staying competitive and sustainable.