Understanding Embedded Systems Design: A Simple Guide
Embedded systems are computers on a chip. We typically use them without even noticing, in controlling the functions of cars, home appliances, health gadgets, mobile phones, etc.
Now let's discuss Embedded Systems and their functionality.

What Are Embedded Systems?
An embedded system is a computer which processes data and executes only a single specific task within a larger piece of equipment. Unlike personal computers that host multiple applications, these systems are built to perform one single function, including washing machine control or heart rate checking in a smartwatch.
This comprises hardware such as sensors and processors and software the programs that run the unit's operations and processes. These systems make it possible for the device to make intelligent decisions.
Example: How It Works in a Vehicle (Engine Control Unit)
Let's examine how embedded systems enable the engine to run smoothly in the vehicle.
Main Parts Used:
- Microcontroller- It is equipped with the necessary instructions and acts as the brain.
- Sensors- These monitor the temperature of the engine and fuel levels.
- Actuators- These control or move things, like fuel injectors.
- Software- The commands given to the microcontroller are woven into this code.
How It Works (Step-by-Step):
1. Fuel level and engine temperature sensors gather data when the vehicle is in motion.
2. The data from the sensors is evaluated by a microcontroller.
3. Signals to increase or decrease fuel and engine speed are sent.
4. This cycle goes on for the duration ignition is on, ensuring the most optimal driving experience with no disruptions
The use of this system enhances the environmental performance of the engine through smart fuel economy, smooth engine functionalities, and minimised ecological footprints.
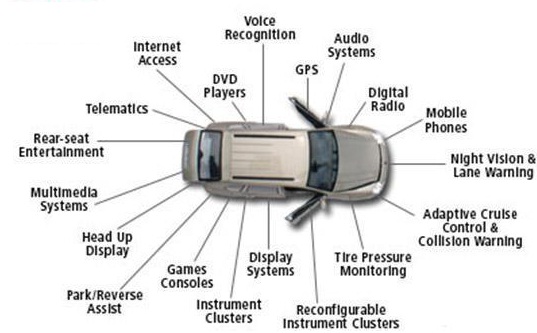
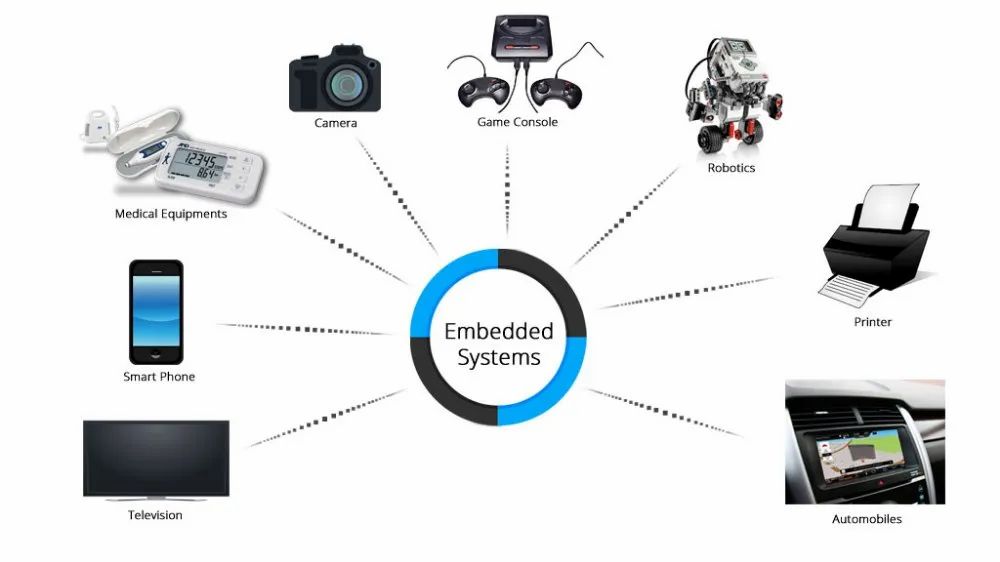
Where Do We Use Embedded Systems?
- Motor Vehicles: For parking aids, engine control and airbags.
- Medical Devices: Pacemakers, infusion pumps, and testing machinery work with precision in hospitals.
- Home Appliances: Smart washing machines, smart refrigerators, and TVs.
- Robotics: Perform computerised, repetitive tasks along with machinery in factories.
- Consumer Electronics: Mobiles, cameras, smart watches and a number of other gadgets are also embedded systems.
Advantages:
• Great at carrying out some specific activities.
• Uses minimum energy.
• Relatively cheap and small in size.
• Dependable for activities that need to be done repetitively.
Disadvantages:
• Has no processing power and limited memory space.
• Difficult to change.
• Can have problems in troubleshooting.
• Automative systems have more freedom and flexibility.
What’s Coming Next?
The next stage will see a rise in the use of smart devices integrated with embedded systems. Examples are self-driving cars, homes, AI in hospitals, and smart drones. These systems will enable communication with one another via the net and will collaborate.
Conclusion:
Embedded systems are important in day-to-day activities without us putting much thought into it. As the technology we use improves, these systems will continue getting smarter and assist us greatly in the future.