Digital Image Processing: A Beginner’s Look
Have you ever wondered how your phone improves a photo automatically or unlocks just by looking at your face? That’s not magic, it’s the work of Digital Image Processing, often called DIP.
DIP is all about helping computers understand and work with images the way humans do. But instead of eyes and brains, machines use code and algorithms.
What Is Digital Image Processing?
Digital Image Processing means using software to read and change digital images. It’s not just about making pictures look better; it’s about pulling out useful details, recognising patterns, and even making decisions based on what’s in the image.

Some common tasks in DIP include:
- Cleaning up blurry or noisy images
- Highlighting edges and shapes
- Adjusting contrast and brightness
- Detecting objects or faces
- Matching patterns or symbols
These actions help machines get useful information from pictures, whether it's a scanned document or a live video feed.
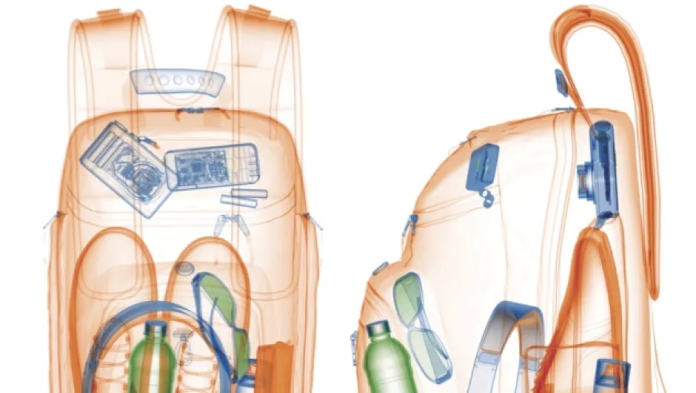
Real-World Example: Airport Security
Think about an airport X-ray scanner. When your bag goes through the machine, a black-and-white image pops up on the screen. But what you do not see is how DIP is working in the background.
It removes extra noise, sharpens the image, and highlights shapes inside the bag. If something matches the shape of a restricted item, the system flags it instantly. This helps security staff act quickly and with better accuracy.

Why It’s Worth Learning
Whether you're a developer, designer, or future AI expert DIP opens doors to a wide range of innovative tech fields like:
- Artificial intelligence
- Robotics
- Augmented and virtual reality
- Healthcare
- Surveillance
Learning DIP helps you understand how machines “see” the world. It also builds a strong base for careers in computer vision and automation.
Where It’s Used
- Medical Fields: Cleaning up scans like X-rays or MRIs
- Agriculture and Weather: Studying satellite images
- Security Cameras: Detecting movement or faces in videos
- Photography Apps: Auto-enhancing pictures
- Banking: Verifying signatures and scanned documents
- Biometric Systems: Face, fingerprint, and iris recognition
Pros and Cons
What’s Good:
- Makes images clearer and more useful
- Helps automate visual tasks
- Speeds up decision-making in machines
What’s Challenging:
- Needs a good grip on image formats and algorithms
- High-quality processing may require strong hardware
- Doesn’t always work well with poor images
Conclusion
Digital Image Processing is the link between the visual world and smart technology. It teaches machines to see and react, just like humans do. Whether you’re building a robot or developing a camera app, understanding DIP can take your skills to the next level.
Ready to dive in? Start your DIP journey today with fun tutorials and real-life examples.