Microprocessors and Microcontrollers: The Brains Behind Smart Machines
Every smart device you use from your washing machine to your mobile phone has something inside that tells it what to do. That something is either a microprocessor or a microcontroller.
They may be tiny, but they do the heavy thinking behind your daily tech. If you're someone who loves tech or wants to build smart devices, understanding microprocessors and microcontrollers is your first step.
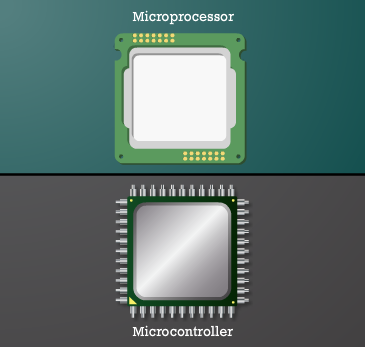
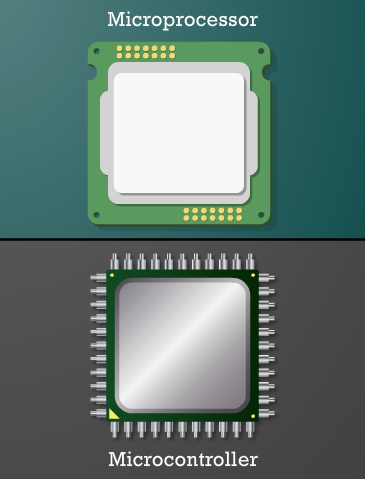
What Are Microprocessors and Microcontrollers?
A Microprocessor is the central brain of a computer system. It can perform many tasks and is designed to work with other external components like memory and input-output devices. You’ll often find it in computers, servers, and high-performance devices.
A Microcontroller, on the other hand, is a compact system on a chip. It contains a processor, memory, and input-output ports all in one. It’s perfect for small, single-purpose systems like digital clocks or smart fans.
Real-Life Scenario: Automatic Water Dispenser
Let’s say you have a sensor-based water dispenser.
- A microcontroller is used here to control the entire process.
- It senses your hand near the tap, opens the valve, and stops when your hand moves away.
- It doesn’t need to do complex calculations just responds to input quickly and reliably.
But in a smart vending machine, which handles touchscreens, card readers, pricing, and customer data a microprocessor would be better due to its ability to multitask and process large amounts of data.


Why Should You Learn This?
- Helps you understand how smart systems are designed
- Useful in building projects like robots, smart meters, and devices
- Unlock career paths in electronics, embedded systems, and automation
- Lay a strong foundation for advanced topics like IoT, robotics, and AI hardware
- A great skill to have for both hardware and software enthusiasts
What You’ll Learn to Do
- Understand the internal structure and working of processors
- Program microcontrollers to perform specific tasks
- Interface sensors, motors, and displays with controllers
- Build systems like line-following robots or temperature control units
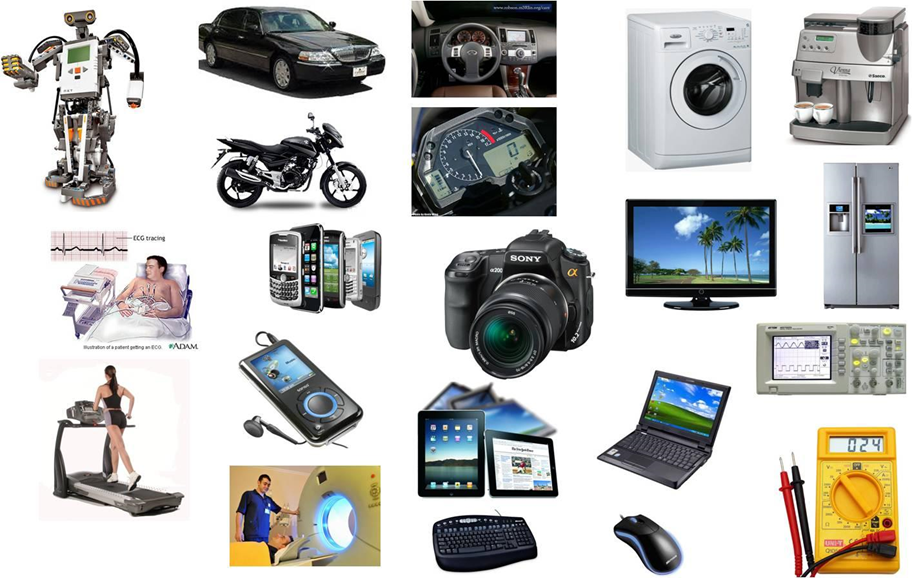
Where These Are Used
- Home Appliances – Washing machines, ovens, microwave timers
- Automobiles – Engine control, anti-lock brakes, airbag systems
- Healthcare – Heartbeat monitors, glucose tracking systems
- Consumer Gadgets – Smartwatches, digital thermometers
- Industry – Conveyor belts, robotic arms, automatic counters

Advantages
- Microcontrollers are compact, cost-effective, and energy-efficient
- Microprocessors are powerful and handle complex computing tasks
- Both are customizable and programmable for specific applications
- Widely used in DIY, academic, and professional tech projects
- Enable faster automation and real-time control
Drawbacks
- Microcontrollers can’t handle large applications or multitasking well
- Microprocessors need extra components to function fully
- Both require some technical background to get started
- Troubleshooting can be difficult without the proper tools
- Memory and processing speed vary depending on the use case
Conclusion
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers may seem small, but they’re at the heart of all modern electronics. From simple devices to advanced systems, these chips make things smart and responsive.
If you’re someone who wants to build, innovate, or just understand how machines think this is where your journey begins.
Start Learning Microprocessors and Microcontrollers

Stop reading dry textbooks. Learn through videos, real-world simulations, and quizzes all in one platform.