Switching Techniques - Packet Switching
Switching Techniques – Packet Switching
In the digital age, where data transmission is crucial for communication, efficient techniques to manage data flow are essential. One such powerful technique is Packet Switching. Let’s explore this concept and understand how it shapes modern networking.
What is Packet Switching?
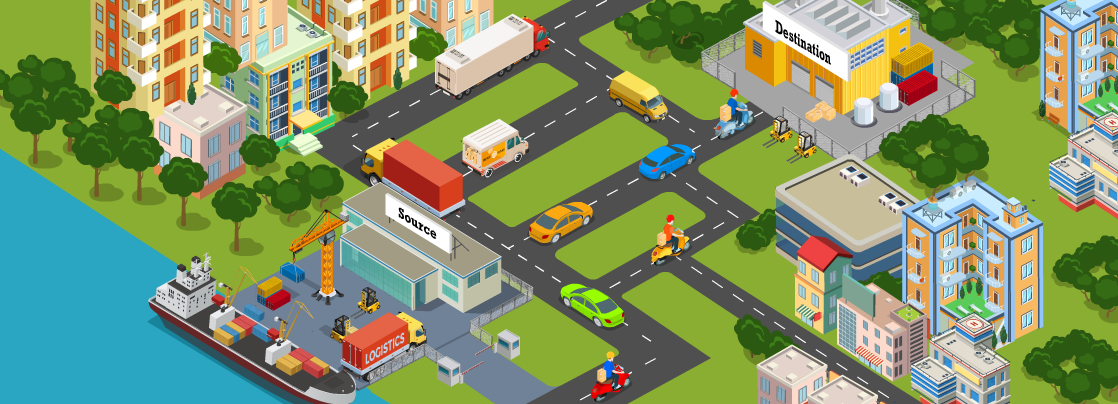
Imagine sending a long message through multiple couriers, where each courier carries only a small part of the message and takes different routes to the recipient. This is how packet switching works in communication networks.
Instead of sending data in one large chunk, the message is broken into smaller pieces called packets. Each packet carries important details like;
- The sender’s and receiver’s IP addresses
- Total number of packets
- The order in which the packets should be arranged
These packets do not follow a dedicated path. Instead, they take the best available route at that moment, often arriving at different times and in a random order. The destination device then reassembles them correctly to recreate the original message.
Why Use Packet Switching?
Packet switching optimises network usage by dynamically using available paths. This makes it perfect for the internet, emails, and video streaming, where data must flow without waiting for a fixed channel.
Advantages of Packet Switching
- Efficient Network Utilisation: The network resources are used as needed rather than being tied up with a single communication.
- Robust and Reliable: Even if one route fails, packets can be redirected through alternative paths.
- Supports Data Bursts: Ideal for applications like video calls where data is transmitted intermittently.
Disadvantages of Packet Switching
- Delay in Reassembly: Since packets may take different routes, they can arrive at different times, requiring reassembly at the destination.
- Packet Loss or Corruption: If packets are lost or corrupted, the message can become incomplete or distorted.
- Overhead: Each packet must carry additional information (headers), which can increase the total data size.
Conclusion
Packet switching is a cornerstone of modern digital communication, offering a dynamic and efficient way to transmit data over complex networks. Its ability to handle multiple data streams simultaneously makes it essential for the Internet and various real-time applications.
Understanding packet switching helps in appreciating the robustness of our connected world, where data flows seamlessly, regardless of the route it takes.