List Slicing in Python
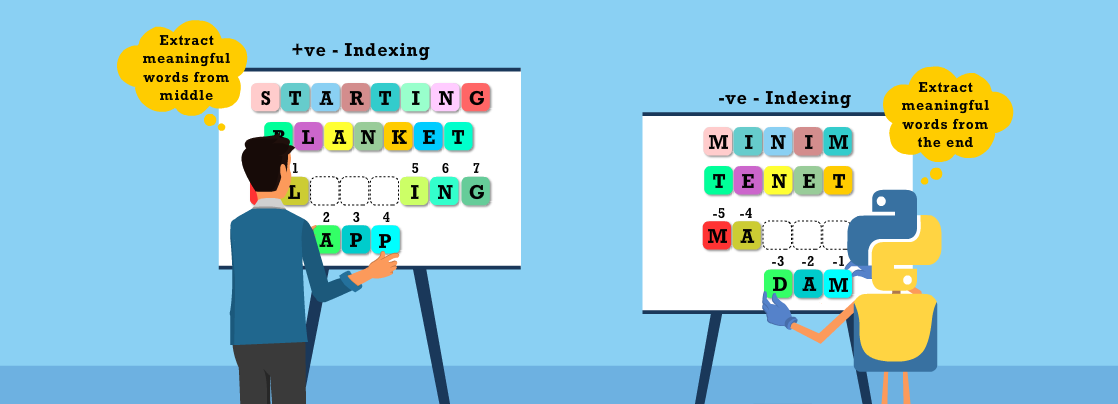
List slicing in Python is a powerful tool for manipulating data sequences, making data handling easier. Imagine you have a long word and you want to remove a few letters from it to form a new word. With positive indexing, you can trim letters from the beginning of the word. On the other hand, negative indexing lets you work from the end. This approach is incredibly versatile for data handling in Python. So, using list slicing, you can quickly and effectively extract parts of your data without loops or additional logic. It's like having a pair of digital scissors that cut exactly where you want them to.
Understanding List Slicing
Python lists support slicing using the colon (:) operator. The basic format is;
list[start:stop:step]
- Start – The index where slicing begins.
- Stop – The index where slicing ends (exclusive).
- Step – The interval between elements (optional).
Examples of List Slicing
Basic Slicing
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
print(numbers[1:4]) # Output: [20, 30, 40]
Extracts elements from index 1 to 3.
Using Negative Indices
print(numbers[-4:-1]) # Output: [30, 40, 50]
Slicing can be done from the end using negative indices.
Skipping Elements with Step
print(numbers[0:6:2]) # Output: [10, 30, 50]
The step value 2 selects every second element.
Reversing a List Using Negative Step
print(numbers[: :-1]) # Output: [60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10]
A step of -1 reverses the list.
Advantages of List Slicing
- Efficient Data Extraction – Retrieves specific elements quickly.
- No Need for Loops – Reduces code complexity.
- Supports Positive and Negative Indices – Allows flexible selection of elements.
- Flexible List Updates - Allows you to modify or replace multiple elements in a list in a single operation.
Modifying a List Using Slicing
List slicing can be used to update multiple elements at once.
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"]
fruits[1:3] = ["grape", "kiwi"]
print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'grape', 'kiwi', 'date']
Elements at index 1 and 2 are replaced.
Conclusion
List slicing simplifies list manipulation in Python. It allows efficient selection, modification, and retrieval of elements using index-based operations. Mastering list slicing helps in writing concise and effective Python programmes.