
Can Engineering Save the Planet?
Introduction to Sustainable Engineering
What if the buildings you live in, the vehicles you use, and even the products you throw away could be redesigned to protect the planet instead of harming it?
That’s not just a futuristic idea. It is the foundation of Sustainable Engineering.
As global challenges like climate change, resource depletion, and pollution intensify, engineers are leading the way with smarter, cleaner, and more responsible solutions.
What Exactly Is Sustainable Engineering?
Sustainable engineering blends innovation with responsibility. It is the practice of designing systems, buildings, processes, and products that reduce environmental impact, use resources efficiently, and promote social and economic well-being. It goes beyond making systems efficient. It ensures they are safe, ethical, and designed with the planet in mind.
Applications of Sustainable Engineering
Sustainable engineering is applied in various sectors to reduce harm and enhance efficiency:
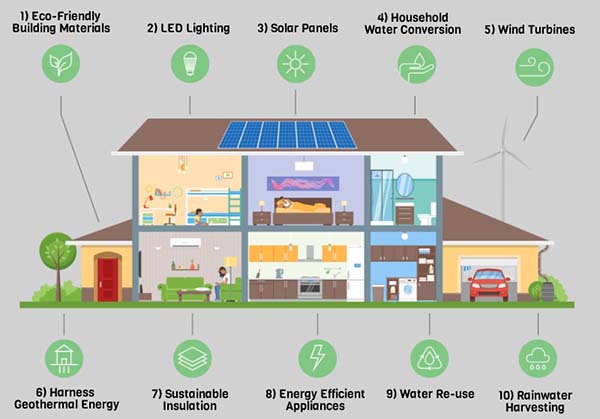
Green Buildings
Engineers design homes and offices with features like:
- Solar panels
- Natural lighting
- Energy-efficient materials
- Rainwater harvesting systems
Sustainable Transportation
- Electric and hybrid vehicles
- Shared mobility systems
- Bicycle-friendly infrastructure
- Urban transport planning to reduce congestion
Industrial Design
- Material selection to minimise waste
- Recyclable components
- Pollution prevention during manufacturing
Environmental Protection
- Treatment of water pollutants
- Radioactive waste management
- Solid waste reduction technologies
Urban Planning
- Smart cities
- Low-emission zones
- Sustainable infrastructure that supports population growth
Eco-Friendly Packaging
- Plant-based alternatives to plastic
- Biodegradable materials
- Reusable designs
Advantages of Sustainable Engineering
- Reduced use of water, energy, and raw materials
- Cleaner air, water, and soil
- Long-term cost savings through efficiency
- Improved public health and quality of life
- Promotes international environmental cooperation and standards
Challenges and Disadvantages
- High initial costs for green systems and materials
- Requires interdisciplinary planning and assessments
- Limited awareness or resistance in some regions
- Legal and policy gaps in environmental regulation
Conclusion
Sustainable engineering is the bridge between innovation and responsibility. It is not just about reducing harm. It is about designing systems that regenerate and support life. Whether you are designing a building, a water treatment plant, or a city-wide transport system, sustainable thinking ensures that today’s solutions don’t become tomorrow’s problems. As future engineers, learning about carbon credits, green buildings, cleaner production, and environmental management standards is essential.







